Embracing Sustainability: Exploring the Wonders of Bioclimatic Design
Bioclimatic Design: Creating Sustainable and Comfortable Spaces
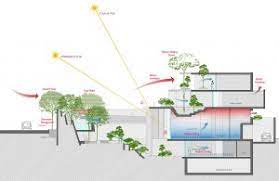
Bioclimatic design is an innovative approach to architecture that focuses on creating buildings that are in harmony with the environment. It takes into account local climate conditions, natural resources, and the use of sustainable materials to maximize energy efficiency and create comfortable living spaces.
One of the key principles of bioclimatic design is passive design strategies. These strategies aim to utilize natural elements such as sunlight, wind, and vegetation to regulate temperature, lighting, and ventilation within a building. By harnessing these natural resources effectively, bioclimatic design reduces the need for artificial heating, cooling, and lighting systems.
In warmer climates, bioclimatic design incorporates features such as shading devices, thermal insulation, and natural ventilation to keep indoor spaces cool. This can include using overhangs or awnings to block direct sunlight while still allowing for natural light to enter the building. Additionally, proper insulation helps maintain a comfortable indoor temperature by reducing heat transfer through walls and roofs. Natural ventilation systems utilize prevailing winds or stack effect to circulate fresh air throughout the building.
In colder climates, bioclimatic design focuses on capturing and storing solar energy through passive solar heating techniques. This can involve positioning windows strategically to allow maximum sunlight penetration during winter months while minimizing heat loss. Thermal mass materials such as concrete or stone are often used in construction to absorb heat during the day and release it slowly at night.
Another aspect of bioclimatic design is the use of sustainable materials. Building materials that have low embodied energy (the total energy required for their production) are preferred in order to reduce the carbon footprint of the construction process. Additionally, materials that are recyclable or biodegradable are chosen to minimize waste and promote a circular economy.
Bioclimatic design also considers the surrounding landscape and ecosystems. It seeks to minimize the impact of construction on natural habitats and preserve biodiversity. By integrating green spaces, such as gardens or living walls, into the building design, bioclimatic architecture can enhance air quality, provide insulation, and create a more pleasant environment for occupants.
The benefits of bioclimatic design are manifold. Not only does it contribute to reducing energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions, but it also enhances occupant comfort and well-being. Buildings designed with bioclimatic principles have been shown to have improved indoor air quality, acoustics, and natural lighting conditions. Moreover, these sustainable designs often result in long-term cost savings due to reduced energy bills.
As our world faces increasing environmental challenges, adopting bioclimatic design principles is crucial in creating a sustainable future. By integrating nature into our built environment and utilizing natural resources wisely, we can create buildings that are not only aesthetically pleasing but also environmentally responsible.
Essential Insights into Bioclimatic Design: Understanding Principles, Strategies, and Benefits for Sustainable Buildings
- What is bioclimatic design?
- How does bioclimatic design contribute to sustainability?
- What are the key principles of bioclimatic design?
- What are some examples of passive design strategies used in bioclimatic design?
- What are the benefits of implementing bioclimatic design in buildings?
What is bioclimatic design?
Bioclimatic design is an innovative approach to architecture that aims to create buildings that are in harmony with the environment. It takes into account local climate conditions, natural resources, and the use of sustainable materials to maximize energy efficiency and create comfortable living spaces. By utilizing passive design strategies and harnessing natural elements such as sunlight, wind, and vegetation, bioclimatic design reduces the need for artificial heating, cooling, and lighting systems. This sustainable design approach not only contributes to reducing energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions but also enhances occupant comfort and well-being.
How does bioclimatic design contribute to sustainability?
Bioclimatic design plays a pivotal role in promoting sustainability by maximizing energy efficiency and minimizing the environmental impact of buildings. By harnessing natural elements such as sunlight, wind, and vegetation, bioclimatic design reduces reliance on artificial heating, cooling, and lighting systems. This approach significantly lowers energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions associated with building operations. Additionally, the use of sustainable materials with low embodied energy and recyclability further reduces the carbon footprint of construction. Bioclimatic design also considers the preservation of ecosystems and biodiversity by integrating green spaces into building design. Ultimately, this holistic approach to architecture creates sustainable spaces that prioritize environmental responsibility without compromising on comfort or aesthetic appeal.
What are the key principles of bioclimatic design?
The key principles of bioclimatic design revolve around creating sustainable and energy-efficient buildings that harmonize with the local climate. These principles include passive design strategies that utilize natural elements like sunlight, wind, and vegetation to regulate temperature, lighting, and ventilation. By maximizing the use of these resources, bioclimatic design minimizes reliance on artificial heating, cooling, and lighting systems. Additionally, the use of sustainable materials with low embodied energy and consideration for the surrounding landscape are integral to bioclimatic design. The goal is to create comfortable living spaces while minimizing environmental impact and promoting a healthier future.
What are some examples of passive design strategies used in bioclimatic design?
Passive design strategies play a vital role in bioclimatic design, allowing buildings to harness natural elements for optimal energy efficiency and comfort. Some examples of passive design strategies commonly employed in bioclimatic design include proper building orientation to maximize solar gain or shade, the use of thermal insulation to reduce heat transfer, natural ventilation systems to promote airflow and cooling, and the incorporation of shading devices such as overhangs or awnings to block direct sunlight. These strategies work together harmoniously to create sustainable and comfortable spaces while minimizing reliance on artificial heating, cooling, and lighting systems.
What are the benefits of implementing bioclimatic design in buildings?
Implementing bioclimatic design in buildings offers numerous benefits. Firstly, it significantly reduces energy consumption by utilizing natural resources such as sunlight, wind, and vegetation to regulate temperature, lighting, and ventilation. This leads to lower utility bills and a reduced carbon footprint. Secondly, bioclimatic design enhances occupant comfort by creating spaces that are naturally lit, well-ventilated, and thermally comfortable throughout the year. Improved indoor air quality and acoustics further contribute to a healthier living or working environment. Additionally, bioclimatic design promotes the use of sustainable materials and construction practices, minimizing waste and supporting a more circular economy. Overall, implementing bioclimatic design in buildings not only benefits the environment but also enhances the well-being and satisfaction of occupants while reducing long-term operational costs.
