Maximizing Efficiency and Comfort with Passive Sustainable Design
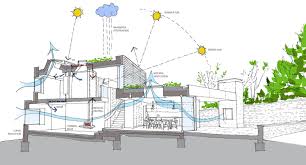
The Benefits of Passive Sustainable Design
Passive sustainable design is an innovative approach to building and construction that focuses on maximizing energy efficiency and minimizing environmental impact. This design philosophy utilizes natural resources such as sunlight, wind, and thermal mass to create comfortable living spaces while reducing the need for artificial heating, cooling, and lighting.
There are several key benefits to incorporating passive sustainable design principles into your building projects:
- Energy Efficiency: Passive sustainable design reduces the reliance on mechanical systems for heating and cooling, resulting in lower energy consumption and cost savings over time.
- Comfort: By optimizing natural light and ventilation, passive sustainable design creates comfortable indoor environments that promote well-being and productivity.
- Environmental Impact: By reducing energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions, passive sustainable design helps mitigate climate change and minimize the ecological footprint of buildings.
- Durability: Passive sustainable design often incorporates durable materials and construction techniques that enhance the longevity of buildings, reducing maintenance costs in the long run.
- Aesthetics: Passive sustainable design can be visually appealing, with features such as large windows for natural light, green roofs for insulation, and passive solar heating elements that enhance the architectural beauty of a structure.
Whether you are designing a new home, office building, or commercial space, incorporating passive sustainable design principles can lead to a more efficient, comfortable, and environmentally friendly built environment. Consult with architects and designers experienced in passive sustainable design to explore innovative solutions tailored to your specific needs and goals.
Embrace the future of architecture with passive sustainable design!
8 Benefits of Passive Sustainable Design: Energy Efficiency, Cost Savings, and More
- Energy efficiency
- Cost savings on utilities
- Improved indoor air quality
- Reduced environmental impact
- Enhanced occupant comfort
- Long-term durability of structures
- Natural light and ventilation benefits
- Aesthetic appeal and architectural innovation
Challenges of Passive Sustainable Design: Initial Costs, Applicability Limits, Complexity, Maintenance, and Climate Sensitivity
Energy efficiency
Energy efficiency is a key benefit of passive sustainable design, as it reduces the reliance on mechanical systems for heating and cooling, resulting in lower energy consumption and cost savings over time. By harnessing natural resources such as sunlight and thermal mass, passive sustainable design optimizes energy usage within buildings, creating environmentally conscious spaces that promote sustainability and reduce the overall carbon footprint.
Cost savings on utilities
Passive sustainable design offers significant cost savings on utilities by optimizing natural resources to reduce energy consumption. By harnessing natural light, ventilation, and thermal mass effectively, buildings designed with passive sustainable principles require less artificial heating, cooling, and lighting. This translates to lower utility bills for occupants over the long term, making passive sustainable design not only environmentally friendly but also economically beneficial. Investing in passive sustainable design can lead to substantial savings on utility expenses while promoting energy efficiency and sustainability.
Improved indoor air quality
Passive sustainable design offers the significant benefit of improved indoor air quality by incorporating natural ventilation strategies and non-toxic building materials. By maximizing airflow through well-placed windows, vents, and passive cooling techniques, passive sustainable design helps reduce indoor pollutants, allergens, and moisture buildup. Additionally, using eco-friendly materials that are low in volatile organic compounds (VOCs) contributes to a healthier indoor environment for occupants. This emphasis on clean air not only enhances occupant health and well-being but also promotes a more comfortable and productive living or working space.
Reduced environmental impact
Passive sustainable design offers the significant benefit of reducing environmental impact by minimizing energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions associated with building operations. By harnessing natural resources like sunlight and wind for heating, cooling, and ventilation, passive sustainable design decreases the reliance on fossil fuels and electricity, thus lowering carbon footprints and contributing to a more sustainable built environment. This proactive approach aligns with global efforts to combat climate change and promotes a greener, healthier planet for future generations.
Enhanced occupant comfort
Passive sustainable design offers the significant benefit of enhanced occupant comfort by creating indoor environments that prioritize the well-being and satisfaction of building occupants. By optimizing natural light, ventilation, and thermal mass, passive sustainable design ensures that spaces maintain consistent temperatures, adequate airflow, and ample natural light throughout the day. This results in a more pleasant and comfortable living or working environment for occupants, promoting productivity, health, and overall satisfaction with their surroundings. The focus on occupant comfort in passive sustainable design contributes to creating spaces that people can truly enjoy and thrive in.
Long-term durability of structures
Passive sustainable design offers the significant advantage of ensuring the long-term durability of structures. By incorporating durable materials, efficient construction techniques, and proper insulation, passive sustainable buildings are built to last. This longevity not only reduces maintenance costs over time but also minimizes the need for frequent repairs and renovations, contributing to a more sustainable and resilient built environment. Investing in passive sustainable design today means enjoying structurally sound buildings that can withstand the test of time, providing lasting benefits for both occupants and the environment.
Natural light and ventilation benefits
Natural light and ventilation are key benefits of passive sustainable design that enhance the overall quality of indoor spaces. By strategically incorporating features such as large windows, skylights, and atriums, natural light floods the interior, creating a bright and inviting atmosphere while reducing the need for artificial lighting during the day. This not only saves energy but also promotes a healthier environment by providing occupants with access to sunlight, which has been linked to improved mood, productivity, and overall well-being. Additionally, proper ventilation design allows for the efficient flow of fresh air throughout the building, improving air quality and thermal comfort without relying on mechanical systems. The integration of natural light and ventilation in passive sustainable design not only reduces energy consumption but also creates spaces that are aesthetically pleasing, comfortable, and conducive to occupant health and happiness.
Aesthetic appeal and architectural innovation
Passive sustainable design offers a pro that extends beyond energy efficiency: aesthetic appeal and architectural innovation. By integrating elements such as large windows for natural light, green roofs for insulation, and passive solar heating features, passive sustainable design not only enhances the visual appeal of a building but also fosters architectural creativity and innovation. These design elements not only contribute to the overall beauty of a structure but also showcase how sustainability can be seamlessly integrated into modern architecture, creating visually stunning and environmentally conscious spaces that inspire and captivate.
Initial Cost
One notable con of passive sustainable design is the higher initial cost associated with implementing sustainable features. While passive sustainable design offers long-term cost savings through reduced energy consumption and operational expenses, the upfront investment required for specialized materials, technologies, and design considerations can be a barrier for some project owners. However, it is essential to weigh these initial costs against the potential long-term benefits in terms of energy efficiency, environmental impact, and overall sustainability to make informed decisions that align with both financial and environmental goals.
Limited Applicability
Passive sustainable design, while beneficial in many aspects, faces the con of limited applicability. This design approach may not be suitable for all building types or locations, which can hinder its widespread adoption. Factors such as site orientation, climate conditions, and architectural constraints can impact the effectiveness of passive sustainable design strategies. In some cases, buildings with specific requirements or functions may not fully benefit from passive design principles, leading to challenges in implementing this approach across all projects. It is essential for architects and designers to carefully assess the feasibility and compatibility of passive sustainable design in each unique context to ensure optimal results and address potential limitations effectively.
Complexity
When considering passive sustainable design, one significant drawback to keep in mind is the complexity involved in designing and implementing passive sustainable features. This approach often necessitates specialized knowledge and expertise in areas such as building orientation, thermal dynamics, and natural ventilation strategies. The intricate nature of integrating these features seamlessly into a building design can pose challenges for architects, engineers, and construction teams, potentially leading to increased project timelines and costs. Careful planning and collaboration with experienced professionals are essential to navigate the complexities of passive sustainable design effectively.
Maintenance Challenges
One significant drawback of passive sustainable design is the maintenance challenges associated with certain design elements. While these features offer long-term benefits in terms of energy efficiency and environmental impact, they may demand ongoing upkeep to sustain their effectiveness. Regular maintenance is essential to ensure that passive sustainable design elements continue to operate at peak performance levels and deliver the desired outcomes. Failure to address maintenance needs promptly can lead to decreased efficiency, increased energy consumption, and potential issues with comfort and functionality within the building space. It is crucial for property owners and designers to factor in the maintenance requirements of passive sustainable design elements when implementing these strategies in construction projects.
Climate Sensitivity
Climate Sensitivity is a significant con of passive sustainable design, as the effectiveness of these design principles may be limited by local climate conditions. In extreme climates, such as areas with high humidity, extreme temperatures, or limited sunlight, passive sustainable design strategies may not perform optimally, leading to challenges in maintaining comfortable indoor environments and achieving desired energy efficiency goals. It is crucial for architects and designers to carefully consider the specific climate factors of a region when implementing passive sustainable design solutions to ensure their effectiveness and long-term viability.
